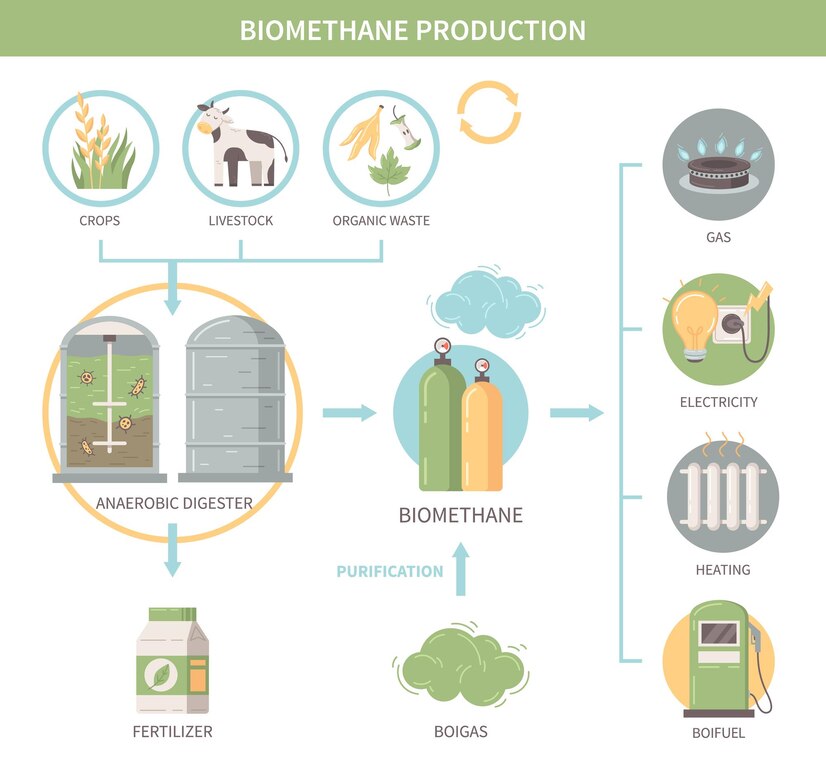
In recent years, the detrimental effects of fossil fuel agriculture have become increasingly apparent, from its contribution to greenhouse gas emissions to soil degradation and water pollution. Transitioning away from this unsustainable practice is crucial for the health of our planet and future generations. In this step-by-step guide, we’ll explore actionable steps to make this transition.
Step 1: Assess Current Practices
The first step in transitioning away from fossil fuel agriculture is to assess your current practices. Evaluate the machinery, fertilizers, and pesticides you use, as well as your irrigation methods and transportation logistics. Identify areas where fossil fuels are heavily relied upon and prioritize these for change.
Step 2: Invest in Renewable Energy
One of the most effective ways to reduce fossil fuel dependency in agriculture is by investing in renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power. Install solar panels on farm buildings, invest in wind turbines for energy generation, or explore options for utilizing bioenergy from organic waste.
Step 3: Adopt Sustainable Farming Practices
Transitioning to sustainable farming practices can significantly reduce reliance on fossil fuels while promoting environmental health. Consider implementing techniques such as crop rotation, cover cropping, and integrated pest management to improve soil fertility and reduce the need for synthetic fertilizers and pesticides.
Step 4: Embrace Precision Agriculture
Utilize precision agriculture technologies to optimize resource use and minimize waste. GPS-guided tractors, drones, and soil sensors can help improve efficiency in planting, irrigation, and fertilizer application, reducing fuel consumption and environmental impact.
Step 5: Explore Alternative Transportation Methods
Reduce the carbon footprint of your farm by exploring alternative transportation methods. Utilize electric or hybrid vehicles for on-farm transportation and consider transitioning to biodiesel or renewable natural gas for larger machinery.
Step 6: Support Local and Organic Food Systems
Support local and organic food systems by sourcing inputs and selling products locally. By reducing the distance traveled from farm to table, you can decrease reliance on fossil fuels for transportation while promoting sustainable agricultural practices in your community.
Step 7: Advocate for Policy Change
Advocate for policy change at the local, regional, and national levels to incentivize sustainable agriculture and renewable energy adoption. Support initiatives that promote renewable energy development, conservation programs, and subsidies for sustainable farming practices.
Step 8: Educate and Collaborate
Educate yourself and others about the benefits of transitioning away from fossil fuel agriculture and collaborate with like-minded individuals and organizations. Join farmer networks, attend workshops, and participate in community initiatives to share knowledge and resources.
Step 9: Monitor Progress and Adapt
Monitor your progress towards reducing fossil fuel dependency and adapt your practices as needed. Regularly assess energy usage, greenhouse gas emissions, soil health, and crop yields to identify areas for improvement and refine your approach over time.
Step 10: Inspire Others
Lead by example and inspire others to join the movement towards sustainable agriculture. Share your experiences, successes, and challenges with fellow farmers, consumers, policymakers, and the broader community to demonstrate the feasibility and benefits of transitioning away from fossil fuel agriculture.
By following these steps and committing to continuous improvement, farmers can play a vital role in mitigating climate change, preserving natural resources, and building resilient food systems for the future.
This comprehensive guide offers practical steps for farmers to transition away from fossil fuel agriculture towards more sustainable practices.
Continuing the Transition: Further Strategies and Considerations
In the previous section, we outlined a step-by-step guide to transitioning away from fossil fuel agriculture. Now, let’s explore some additional strategies and considerations to enhance this transition further.
Integration of Agroecological Principles
Agroecology emphasizes the integration of ecological principles into agricultural production systems. By mimicking natural ecosystems, agroecological practices promote biodiversity, soil health, and resilience to climate change. Incorporating agroecological principles into farming operations can further reduce reliance on fossil fuels while enhancing sustainability and productivity.
Diversification of Farm Enterprises
Diversifying farm enterprises can help reduce dependency on fossil fuels and enhance economic resilience. Consider integrating livestock, agroforestry, or value-added products into your operation to create additional revenue streams and reduce input costs. Diversification can also improve soil health, pest management, and nutrient cycling, reducing the need for external inputs.
Investment in Soil Carbon Sequestration
Soil carbon sequestration involves capturing and storing atmospheric carbon dioxide in agricultural soils. Practices such as no-till farming, cover cropping, and agroforestry can enhance soil organic matter and sequester carbon, mitigating climate change while improving soil fertility and water retention. Investing in soil carbon sequestration can be a powerful tool for reducing greenhouse gas emissions from agriculture.
Collaboration with Researchers and Extension Services
Collaborate with researchers, extension services, and agricultural professionals to access the latest scientific knowledge and technical assistance. Universities, government agencies, and nonprofit organizations often offer resources, funding opportunities, and educational programs to support farmers in transitioning to sustainable practices. By leveraging expertise and networks, farmers can accelerate the transition away from fossil fuel agriculture.
Consumer Education and Market Development
Educate consumers about the environmental and social benefits of sustainable agriculture and support market development for sustainably produced foods. Consumer demand for organic, local, and regeneratively grown products is on the rise, presenting opportunities for farmers to diversify their markets and increase profitability. Engage with consumers through educational events, farm tours, and direct marketing channels to build awareness and loyalty.
Resilience Planning for Climate Change
Develop resilience plans to adapt to the impacts of climate change on agricultural production. Identify potential risks such as extreme weather events, water scarcity, and pest outbreaks, and implement strategies to mitigate these risks. Diversify crops, improve water management infrastructure, and invest in resilient varieties to build adaptive capacity and ensure long-term viability in a changing climate.
Continued Advocacy and Policy Engagement
Continue advocating for policies that support sustainable agriculture, renewable energy, and climate mitigation efforts. Engage with policymakers, industry associations, and advocacy groups to influence legislation, regulations, and funding priorities. Support initiatives that promote agroecological practices, renewable energy development, and equitable access to resources for all farmers.
Evaluation and Reflection
Regularly evaluate progress towards sustainability goals and reflect on lessons learned. Monitor key performance indicators such as energy efficiency, greenhouse gas emissions, biodiversity, and economic viability to track success and identify areas for improvement. Celebrate achievements and share experiences with the farming community to inspire others and foster a culture of continuous improvement.
By incorporating these additional strategies and considerations into your transition away from fossil fuel agriculture, you can further enhance sustainability, resilience, and prosperity on your farm.
This continuation provides additional insights and strategies for farmers looking to deepen their transition away from fossil fuel agriculture.